100% Pass Cisco, PMP, CISA, CISM, AWS Dumps on SALE!
Get Now
01:59:56
X
OSPF routing protocol study notes sharing
Types of OSPF packets
Hello: Used to establish and maintain neighbor relationships. It is sent once every 10 seconds and timed out after 30 seconds.
hello, area-id, authentication, stub
Passive-interface, MTU, and an ACL on the interface filter OSPF traffic
Five OSPF messages
1. HELLO
2. LSU
3. LSR
4. DBD: Directory
5. LSACK
Three tables of OSPF
Topology table (LSDB): the same LSDB in the same area
Neighbor table: also called neighbor state database
Routing table: the best path to the target network
Various types of LSA
Point-to-point broadcast
The reason is because LSDB is not synchronized
Point-to-point does not elect DR, no type 2 LSA
Broadcast has type 1 LSA type 2 LSA
LSA: 1 2 3
L1
Content: This router announces the link information to OSPF,
Who generated it: OSPF router
Scope of spread: Flooding in the area
L2
What routers are in this area
DR
Flooding in the area
L3
LSA in other regions
ABR
Flood to the entire AS, except for special areas
LSA: 4 5 6 7 8 9
Type 4 LSA
Advertise ASBR information
ABR is produced,
Flood to the entire AS, except for special areas
Category 5 LSA
External link information
ASBR generation
Flood to the entire AS, except for special areas
Type 6 LSA is used for MOSPF protocol and used for multicast
Category 7 LSA
External LSA information imported from NSSA area
ASBR generation
7 to 5 process, flooding in the NSSA area
Type 8 LSA, replacing Type 1 LSA in IPv6 network
Type 9 LSA, replace Type 2 LSA in IPv6 network
OSPF routing type
O: Routing in the area Type 1 LSA Type 2 LSA
OIA: Inter-area Routing Type 3 LSA
OE1 OE2: External routing Type 5 LSA
ON1 ON2: Route outside NSSA area Type 7 LSA
OSPF neighbor relationship
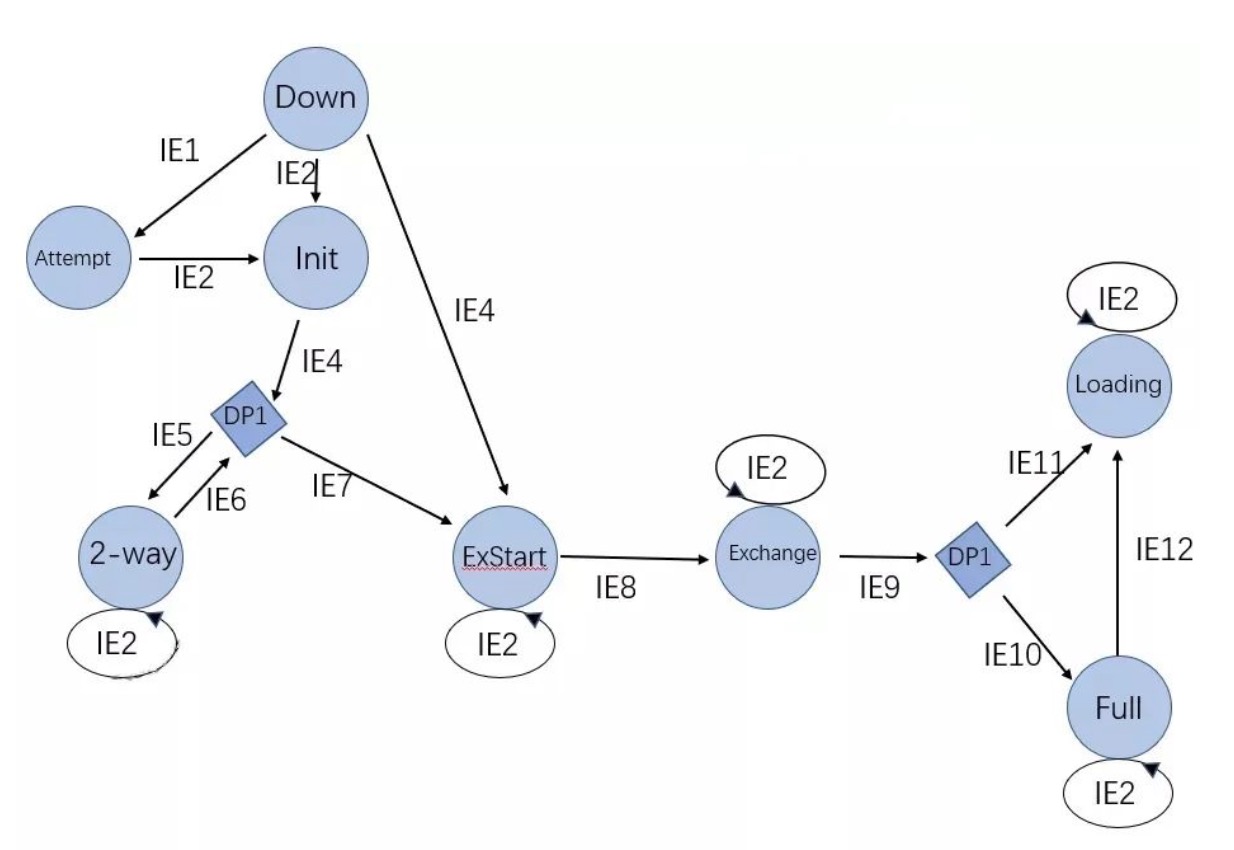
1. Down: In the initial state, no hello packets from neighbors have been received.
2. Attempt: only used in NBMA network, neighbors are valid.
3. Init: Received the neighbor's hello, marking the establishment of its own neighbor relationship table.
4.Two-way: I saw my router id in the neighbor's hello packet and selected DR BDR.
5. Exstart: elect the master and slave routers, the MTU should be consistent.
6. Exchange: send DBD messages.
7. Loading: Exchange LSA information and send LSR LSU LSACK.
8.Full: completely adjacent. Calculate the shortest path synchronously and load the routing table.
OSPF network type
1. Point-to-point: destination IP 224.0.0.5, a pair of routers form an adjacency relationship. Without DR, each sub-interface belongs to a different IP subnet.
2. Point-to-multipoint: destination IP 224.0.0.5, no DR, same IP subnet. PTP and PTMP cannot form an adjacency.
3. Point-to-multipoint non-broadcast: destination IP unicast, no DR, same IP subnet.
4. NBMA: destination IP unicast, select DR, the same IP subnet. Fully or partially interconnected.
5. Broadcast: elect DR, all routers send messages to 224.0.0.6, and then DR sends updates to 224.0.0.5, DR establishes adjacency relationship with all routers, and all DRohter routers converge to 2-way state. The same IP subnet, fully interconnected or partially interconnected.
Summary of features:
1. Whether to elect DR or whether to manually specify neighbors
2. Point family does not need to elect DR and BDR
3. Non-broadcast multiple access NBMA, non-broadcast are unicast updates
4. If this network type cannot deliver multicast, neighbors need to specify manually
5. Looking at the name of the network type, if there is no broadcast, it means that multicast cannot be delivered
Why do you need a virtual link?
The non-backbone area and the backbone area are required to be connected
Why are non-backbone areas and backbone areas connected?
Prevent loops
OSPF relies on SPF algorithm to ensure that there is no loop in an area,
LSDB of each area is synchronized
When to use virtual links?
Backbone areas are isolated by non-backbone areas area 0---area 1 --area 0
The backbone area and the non-backbone area are separated by the non-backbone area area 0---area 2---area3
Authentication method: regional authentication, interface authentication
Authentication type: Clear text authentication MD5 authentication
OSPF route summary type
Route summary between areas area 1 rang
Summary of external routes: summary-address
Configure GTSM under the routing process, which is enabled by default on all OSPF interfaces
Access prefix-list matches route entries
Route-map x permit 10
Match ip address 10
router ospf process-id
prefix-priority low route-map x
fast-reroute per-prefix enable prefix-priority low
The above is the news sharing from the PASSHOT. I hope it can be inspired you. If you think today' s content is not too bad, you are welcome to share it with other friends. There are more latest Linux dumps, CCNA 200-301 dumps, CCNP Written dumps and CCIE Written dumps waiting for you.
Cisco Dumps Popular Search:
300-415 ensdwi training ccie lab 18 months cisco 200-301 guide 300-720 cisco ccna wireless pdf free ccie lab pdf ccie data center version 3.0 cisco certification price ccna practice free ccna certification exam price
Copyright © 2025 PASSHOT All rights reserved.






