100% Pass Cisco, PMP, CISA, CISM, AWS Dumps on SALE!
Get Now
01:59:56
X
Can IPv6 really speed up to 1000 times faster than IPv4?
IPv6 is the next generation of the first generation Internet protocol IPv4, which allows users to have more IP addresses. In theory, IPv6 can allow everyone on the planet to have 16 million IP addresses, and the network speed can be increased by more than 1000 times. "
The above excerpt is selected from a certain website news. IPV6 can really increase the speed by 1000 times? How does it work?
I'm very interested, how is it calculated that each person in the world has 16 million IP addresses? How does the speed increase of 1000 times come out? If no quantitative analysis can be given, it will be publicity and misleading.
How do operators assign IPv6 addresses to ordinary users?
2001: 1: 2: 3: x: x: x: x / 64
Among them, "2001: 1: 2: 3/64" is assigned by the operator, and "x: x: x: x / 64" is automatically configured by the terminal device, which is also a 64-bit, which happens to be a 128-bit IPv6 address.
This means that the user can choose any ID he likes in the space in 264, as long as it does not conflict with the ID of the gateway.
Readers may be surprised, ah, how can operators be so generous and allocate so many IPv6 addresses to users all at once?
In fact, this is not to blame the operators, mainly because there are too many IPv6 addresses. As long as the operator does not use the / 64 netmask to significantly reduce the network segment number, the routing table entries of the Internet router will swell to the point that it cannot be stored and managed.
The question is, can user computers use a longer netmask than / 64? Generally not possible and unnecessary. If the user must configure it, of course, it can also be manually configured, but if the system's automatic configuration is used, the longest netmask is also the only netmask is 64, no more than one, and no less than one.
Where is a longer netmask used?
/ 127 is usually used on the link between P2P routers, but it needs to be manually configured. However, everyone soon discovered that routers will have a large number of / 127 routing entries. Once they enter the global routing table, the global routers will rapidly expand, the table lookup time will increase, and more memory will be required for storage.
To avoid the above bad situation, you need to summarize / 127 or other routes greater than / 64 into routes less than or equal to / 64.
What innovations does IPv6 have over IPv4?
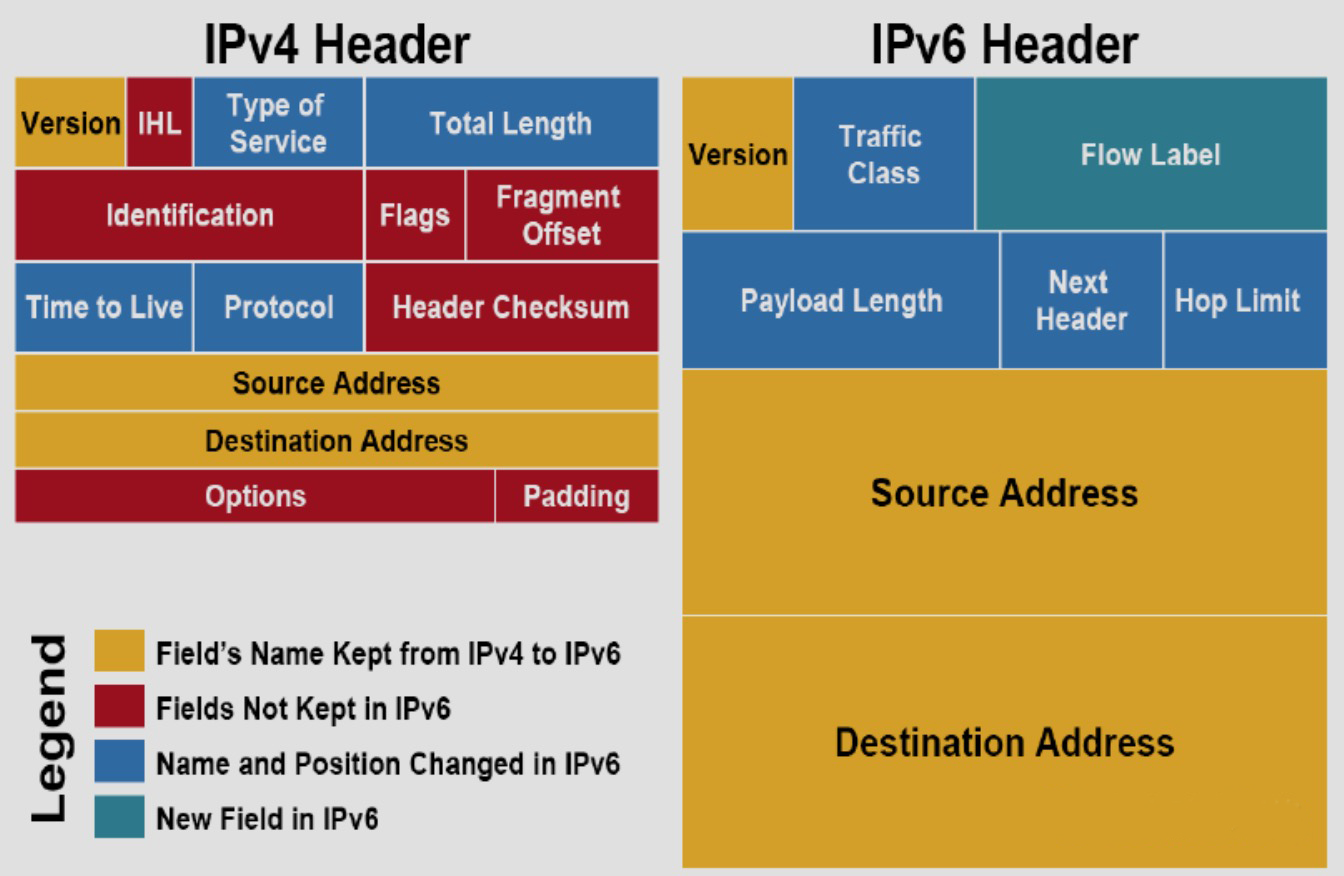
It can be seen from the comparison of the above two protocol headers that the IPv6 protocol header is more concise and streamlined. In summary, there are mainly:
• Does not support IP fragmentation
The source host needs to fragment any outgoing IP packets. The router no longer supports fragmentation.
• IP layer no longer checks packets
Completely rely on the data link layer, transport layer, application layer to complete the data verification work.
• IPv6 header length is fixed
Hardware-based traffic forwarding makes it easier to accelerate.
All the above features make IPv6 gain points in forwarding performance, while reducing the processing dwell time of IPv6 packets inside the router, and the end-to-end RTT delay will gain a small gain. But it is a joke to say that IPv6 will increase 1000 times faster than IPv4.
The speed of the Internet mainly depends on the speed of the physical link. The maximum bandwidth provided by a 1Gbps link is 1Gbps, whether it is IPv4 or IPv6, provided that the router forwarding rate is not a bottleneck. The difference between the two is only IP The internal residence time of the message.
This article may have been written more than 10 years ago. At that time, the speed of Ethernet = 10Mbps. Now the speed of Ethernet = 1000/10000 Mbps. It is commonplace. .
At present, IPv6 only uses 3/2000 as a test field. Once IPv6 is rolled out on a large scale, many engineers face the danger of knowledge faults. The mature technical branches of IPv6 addresses are: EUI-64, HASH, Manual, and CGA. Each technology branch has its own application scenarios. Understanding the application scenarios will understand these technical branches.
The above is the news sharing from the PASSHOT. I hope it can be inspired you. If you think today' s content is not too bad, you are welcome to share it with other friends. There are more latest Linux dumps, CCNA 200-301 dumps and CCNP Written dumps waiting for you.
Cisco Dumps Popular Search:
spoto exam dump 200-301 flashcards 350-801 pdf new ccna review ccie lab update ccna certification university of phoenix ccnp switch dumps pdf ccna official cert guide 200 301 cbt nuggets ccnp 350 401 ccie lab locations
Copyright © 2025 PASSHOT All rights reserved.






