100% Pass Cisco, PMP, CISA, CISM, AWS Dumps on SALE!
Get Now
01:59:56
X
Why the application layer need to do data integrity checks?
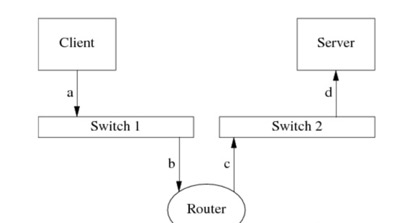
The CRC32 of the Ethernet is relatively strong, but it can only guarantee that the communication on the same network segment will not be wrong (the network cables of the two machines are plugged into the same switch, and the CRC of the Ethernet is useful at this time). But what if there is a multi-level router between the two machines?
I know that within the same Ethernet domain, the CRC32 field at the end of the FCS of Ethernet will ensure data integrity, but the author said that data transmitted between multi-level routers cannot guarantee data integrity. What is the reason? Is it because "the transmission between multi-level routers is not the Ethernet protocol stack used, so there is no algorithm such as CRC32?"
So the question arises, why isn't the integrity check done for transmissions between routers? If every transmission link of the entire link has a check algorithm similar to CRC, can the upper layer be omitted from the data check? Why is this not done in practice? Is it a cost factor?
Another question is, now that the MAC frame has a CRC32 check, why does the UDP packet at the transport layer still have a checksum field?
Pharaoh transferred 1,000 to Lao Zhang through online banking, but the transfer instruction happened to be wrong. The data read by the server was “transfer 9000 to Lao Zhang”. On Wang's computer, it was shown that the transfer was 1,000 yuan. If you are Pharaoh, would you?
Definitely not willing! It may still be dismissive to say that the computer is so reliable and the underlying network transmission also has a check mechanism. How could it be wrong?
Hehe, of course I think so. In daily life, we use online bank transfers, and we never worry that the bank will transfer the wrong amount. Too much immersion in a happy life often makes people take life for granted.
If I tell you, this world is not 100% reliable! Even if the computer makes mistakes, it will make mistakes even if the data is disturbed. There are even malicious man-made changes to the data. Don't you be surprised?
So how do Internet experts ensure data integrity?
Westerners do things like Double Check or even Triple Check. It needs to be repeatedly checked by two or three people to ensure reliability. The idea is that one person may make mistakes, and even two people may make mistakes at the same time, but the probability of three people making mistakes at the same time is very small. This criterion is also used to check the integrity of the data.
Link layer strong check
Often, data leaving the computer and flowing in various media is the most error-prone because the signal will have various interferences. The medium includes network cable, optical fiber, and air. Due to the high probability of error, the data integrity check at the data link layer uses a strong check and a CRC check.
The so-called strong check means that once an error occurs in the data, the CRC check will detect and discard the error with high reliability, and the reliability can reach 1/108.
Ethernet as an example, a frame of data is about 1500 bytes, but the CRC needs to provide integrity for these 1500 bytes, and the value space of the CRC is only 4 bytes! Yes, you read that right, just 4 bytes, but you have to serve 1500 bytes. The number of guests far exceeds the number of waiters, and it is commendable to achieve high reliability.
Weak check at the network layer
It means that the data submitted by the data link layer to the IP layer may be wrong. The submission process is a copy of the data, and errors may be introduced here, as mentioned above. A computer with thick eyebrows and good looks turned out to be wrong, which is really unexpected!
It doesn't matter, does the IP layer still have Checksum verification?
Some students will say that CRC is a non-linear, high-level check algorithm, and Checksum is only a linear, low-level checksum algorithm. CRC did not check out, can you checksum?
The ruler has a length, and the inch has a short length. It's hard to say whether Checksum can check the CRC omission. But if I tell you, the main purpose of the checksum of the IP layer is to prevent the copy operation of the data in the computer from generating IP header data error errors. You may not be so entangled. Because the IP check does not cover the data part at all.
The core idea here is that the closer to the origin of the data, discard the wrong data, and avoid the wrong data from attacking thousands of miles and harming network resources.
Weak check at the transport layer
Don't worry, isn't there a TCP / UDP checksum?
The problem is that TCP / UDP is also a weak checksum check. Since it is a weak check, it means that reliability is a concern. Why not use a strong check, such as CRC or MD5 or SHA?
In the era of designing TCP / IP, the computer's computing power is not so powerful. The CRC consumes a large amount of CPU resources, which will make the computer slow down suddenly. However, Checksum is just a simple addition, which consumes less CPU resources, so Checksum wins!
Don't worry, we also have security layer verification!
Security layer super check
The security layer here refers to TLS, which is well known to women and children in the industry. Generally, the check value space of TLS has 16 or 20 bytes, depending on whether it is MD5 or SHA1. If you feel that the reliability is not enough, you can use SHA 512, and the check space can reach 64 bytes.
In addition, the security layer also adds a key when calculating these check values. Only the sender and receiver know that any third party cannot forge. This truly achieves data integrity beyond reliability!
Application-level strong verification
Data is the core element of communication. If the data is wrong, everything is a waste of emotion!
Therefore, as the last pipe card, the application layer should use super-verification as much as possible to maximize the protection of data integrity!
to sum up
If you can only choose three of the five levels of verification, then choose:
• Link layer strong check
• Strong security layer verification
• Application-level strong verification
The above is the news sharing from the PASSHOT. I hope it can be inspired you. If you think today' s content is not too bad, you are welcome to share it with other friends. There are more latest Linux dumps, CCNA 200-301 dumps and CCNP Written dumps waiting for you.
Cisco Dumps Popular Search:
ccna 200-301 cheat sheet pdf itpro tv cisco ccna 200-301 ccna rs pdf ccnp route chris bryant pdf ccna 3 chapter 5 exam answers ccna certification number passleader ccie dc chapter 5 exam ccnp switch cisco 300-710 book 200-301 cisco book
Copyright © 2025 PASSHOT All rights reserved.






